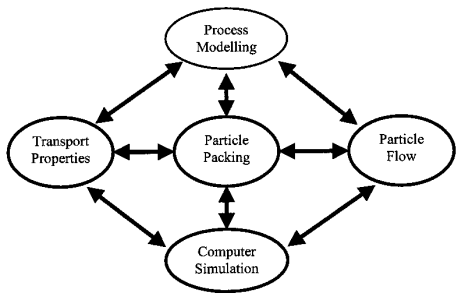
1. Particle Packing Characteristics
-
To understand and model the packing of particles from coarse to fine, from spherical to nonspherical, and from dry to wet systems;
-
To investigate and model the structure of particle packings through rigorous simulation studies, developing a novel theory to describe the relationship between microstructural and macrostructural properties; and
-
To apply the above findings to various industries, with special reference to the quantification of property functions for general application.
2. Transport Phenomena/Properties
-
To study the mechanisms governing transport phenomena, such as fluid flow, heat transfer and mass transfer, in a packed bed at the microscopic (particle-to-particle or pore-to-pore) level through a combined theoretical and experimental effort;
-
To study and quantify particle-particle, particle-fluid, and fluid-fluid interactions under various conditions, generating interfacial interaction laws for the continuum-based modelling of metallurgical/mineral processes; and
-
To apply the above findings to the understanding/modelling of complex multi-phase flow phenomena encountered in industries, e.g. the gas-fluid-powder flow in moving particles under blast furnace conditions.
3. Particle Flow Characteristics
-
To understand the microdynamics of particle and particle-fluid flows through a combined theoretical (supported by advanced numerical techniques) and experimental study;
-
To study the effects of key variables on flow behaviour of particles in relation to different unit operations; and
-
To develop and validate mathematical models, ie governing equations with proper constitutive relationships, to describe solids and coupled fluid flows in particulate and mineral processing.
4. Advanced Simulation/Modelling/Visulisation Techniques
-
Discrete Particle Simulation (DPM): extending the current models from 2D to 3D, monosized to multisized, spherical to nonspherical, coarse to fine, dry to wet, and particle to sub-particle scale, plus visualization technique for DPM application;
-
Continuum-based modelling (often CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics)): development of particle-oriented, robust codes, multi-phase flow modelling; and
-
DPM-CFD modelling/simulation: extending the current modelling from gas-particle to particle-fluid (including gas-liquid) two-phase flow as a whole, from two-phase to multi-phase, from simple to complicated systems.
5. Process Modelling and Application
To apply the results of these investigations to modelling various processes/phenomena in bulk solids handing, mineral processing and process metallurgy. On-going research activities in this direction include:
- Size segregation in particulate processing, e.g. stockpiling;
- Fluid flow, heat and mass transfer in porous media or packed bed reactors;
- Solids flow in process vessels such as hoppers and blast furnaces;
- Multi-phase flow in catalytic reactors, blast furnaces and/or fluidised beds;
- Packing/agglomeration/granulation in iron ore sintering and/or powder processing for advanced materials (ceramic/composite) manufacturing;
- Measurement and modelling of fine particle aggregation;
- Mechanical properties of particulate-based products; and
- CFD applications in mineral, materials and/or environmental engineering.